On 24 – 25 September 2020, the first EU4Ocean workshop– Designing Ocean Literacy action in Europe will be organised by the EU4Ocean Coalition – a new initiative on ocean literacy of the European Commission.

Following the official announcement by the Commissioner for Environment, Oceans and Fisheries, Virginijus Sinkevičius during the first international Virtual Ocean Literacy Summit (World Ocean Day, June 8 2020), founding members of the EU4Ocean Platform have recently kicked-off their work: 76 organisations (including the Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences) and initiatives eager to connect, collaborate and mobilise efforts on ocean literacy. Members gathered online to get to know each other, and shared ideas of collective actions on three priority themes: Climate and Ocean, Food from the Ocean, and Healthy and Clean Ocean.
At the same time, the Youth4Ocean Forum is gathering its founding members, a group of young people aged between 16 and 30 who are passionate about the ocean. Founding members have just met online to join forces to support changes in mindsets and practices across Europe that will contribute to a healthy and sustainable ocean.
This summer, the Network of European Blue Schools is being established to bring the ocean into classrooms – and students to the ocean! Teachers, school managers, marine educators and students will be provided a handbook to help them engage in the “Find the Blue” challenge. Students will create and implement practical action-oriented problem-solving educational projects addressing ocean issues and challenges. Successful projects will earn their school the European Blue School certification.

A diverse community engaged in Ocean Literacy is growing in Europe.
On 24 September, a series of interactive and participatory online workshops will serve as platform for founding members and key stakeholders to present the ambition, organisation, process and tools put in place for supporting collective action for each of the three communities of the EU4Ocean Coalition.
Online workshops planned on 24 September include:
- The EU4Ocean coalition: what, what for, how? (morning)
This webinar will reflect the focus of, and interconnection between, the three communities of the EU4Ocean coalition: the EU4Ocean Platform, the Youth4Ocean Forum and the Network of European Blue Schools. Winners of the #YoungOceanWaves contest will be announced during this online workshop.
- Engaging in the EU4Ocean platform (morning)
This webinar will focus on the need for collective change of understanding, values and actions, as well as on the growing importance of communication and capacity building for effective joint efforts. It will present the first operational work of the EU4Ocean Platform.
- Mobilising the Youth: the Youth4Ocean forum (afternoon)
Youth is a drive for change. The webinar will pave the way for the Forum to operate and promote collaborations between young enthusiastic people.
- The Network of European Blue Schools: embarking on a journey for ocean literacy (afternoon)
Ocean literate children will be responsible adults. In this webinar, schools and teachers will share experiences in Ocean Literacy and identify drivers and pre-conditions for success and key areas for future work. The EU Blue School handbook and certification process will be presented.

September 25 will be dedicated to building momentum for collective actions, mobilising representatives of the three communities at the EU and at the regional sea basin scales in the Baltic, North Sea, Atlantic, Mediterranean & Black Sea basins, which express the EU diversity, cultural richness, and knowledge sharing.
Online workshops planned on 25 September include:
- Building collective Ocean Literacy initiatives at the sea basin scale (morning)
Five parallel online workshops will be co-organised to investigate specific marine and Ocean Literacy challenges in European sea basins. Participants will be encouraged to share their know-how and identify opportunities for collective actions.
- Paving the way to collective initiatives addressing key marine challenges (afternoon)
Combining plenary and parallel group sessions, this workshop aims at setting the basis for collective ocean literacy initiatives on Climate and Ocean, Food from the Ocean, and Healthy and Clean Ocean.
Save the date: 24 – 25 September and join the first EU4Ocean workshop– Designing Ocean Literacy action in Europe!
Bring your ideas, get inspired, and take action for the ocean.
Registration to the event will open soon. Stay tuned!
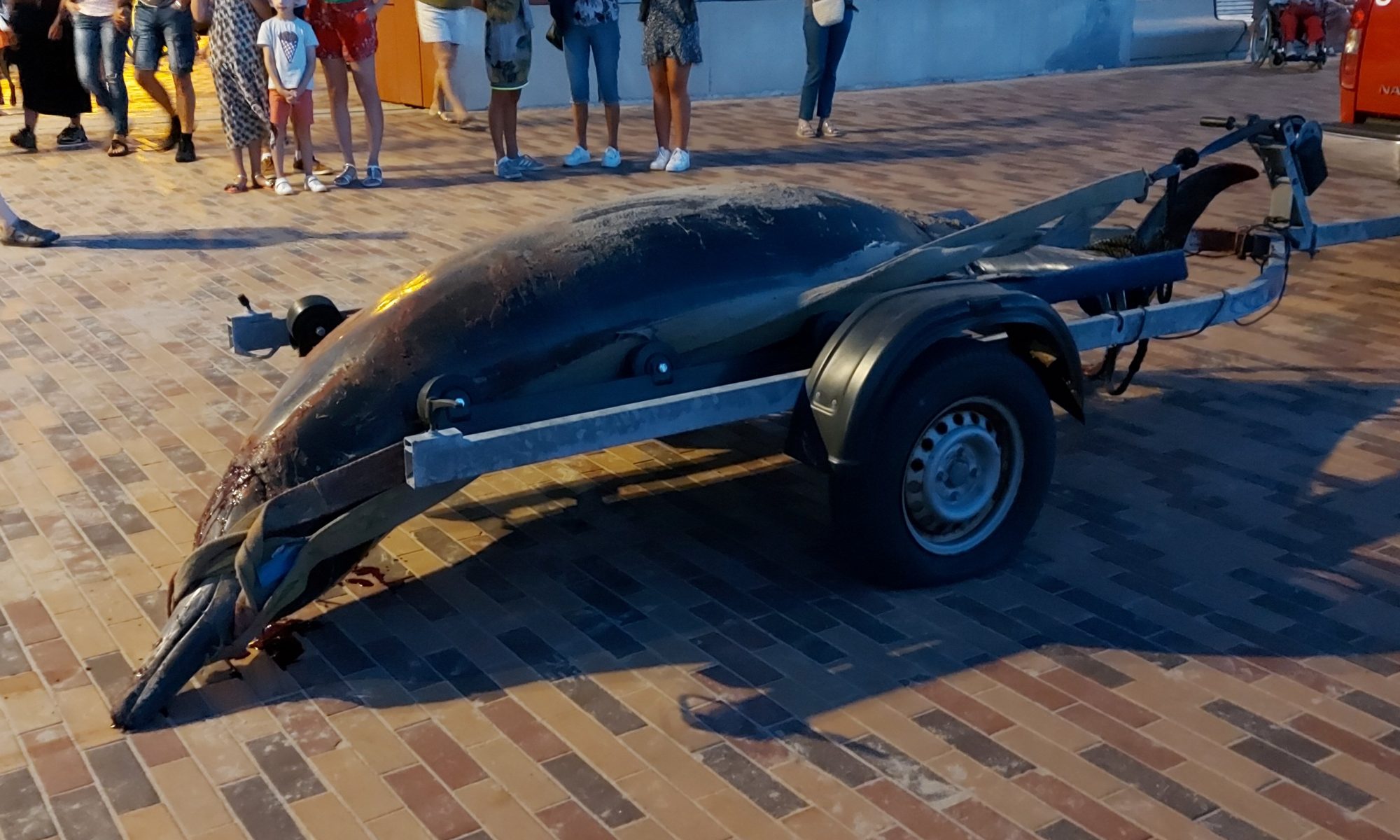
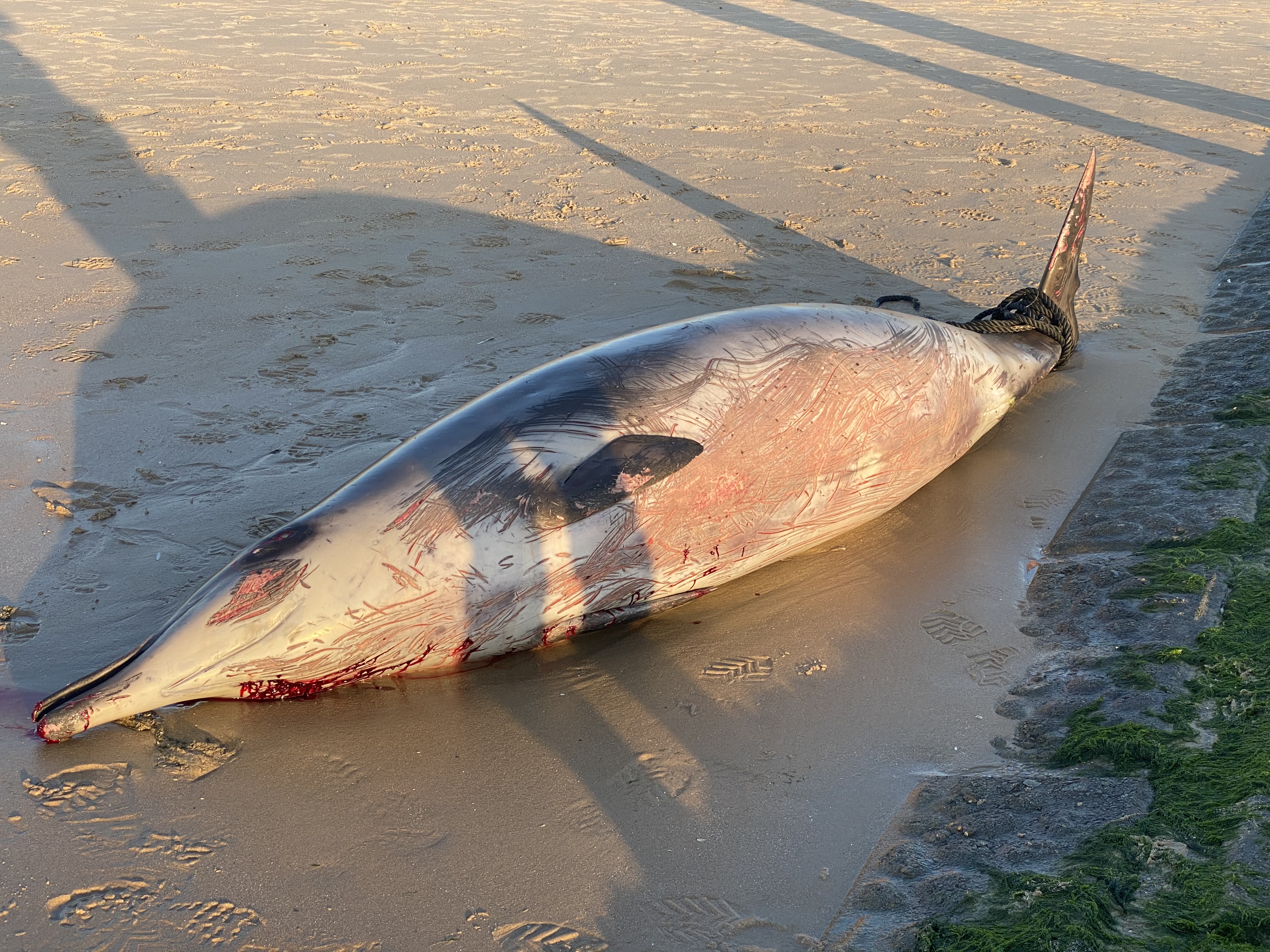
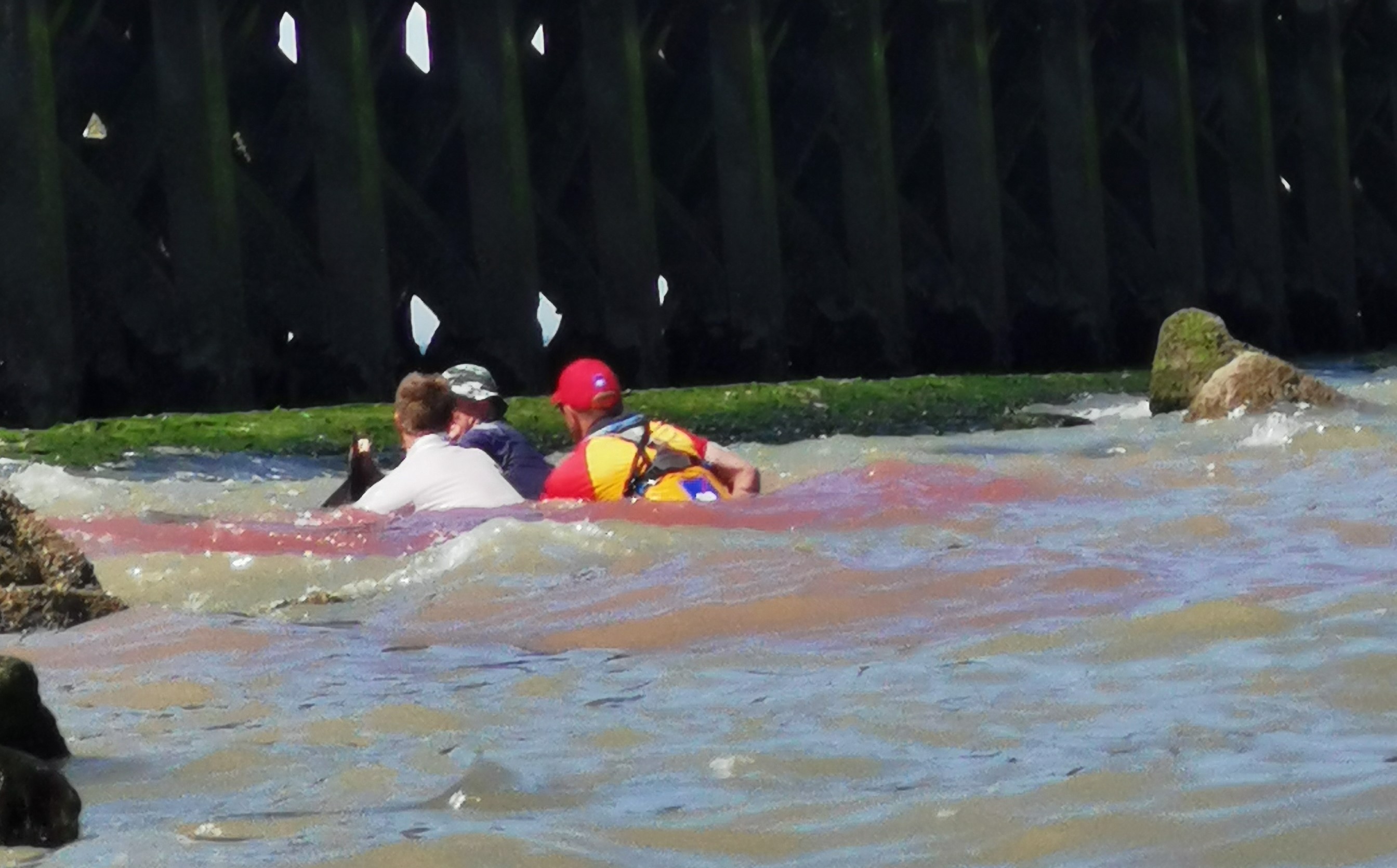
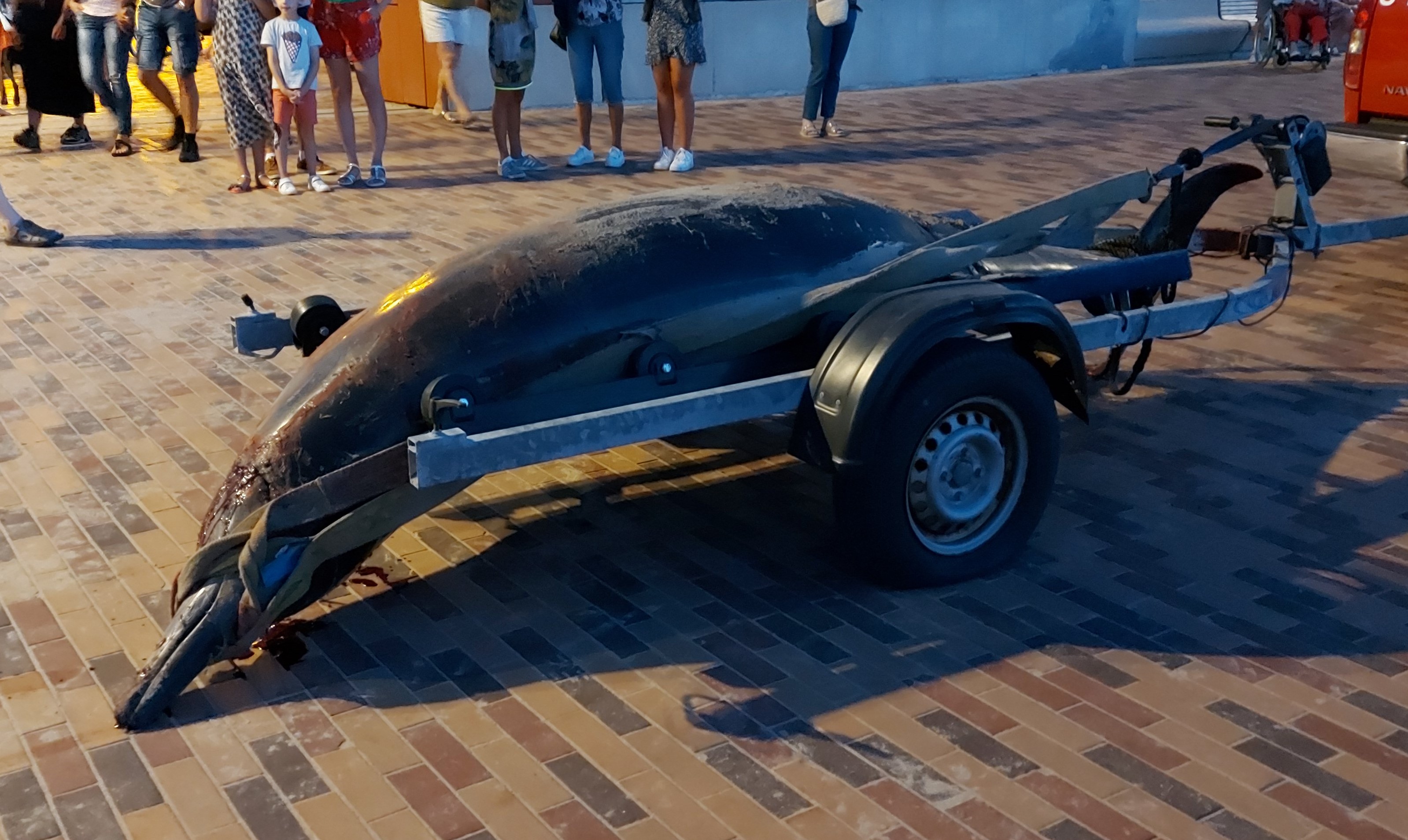
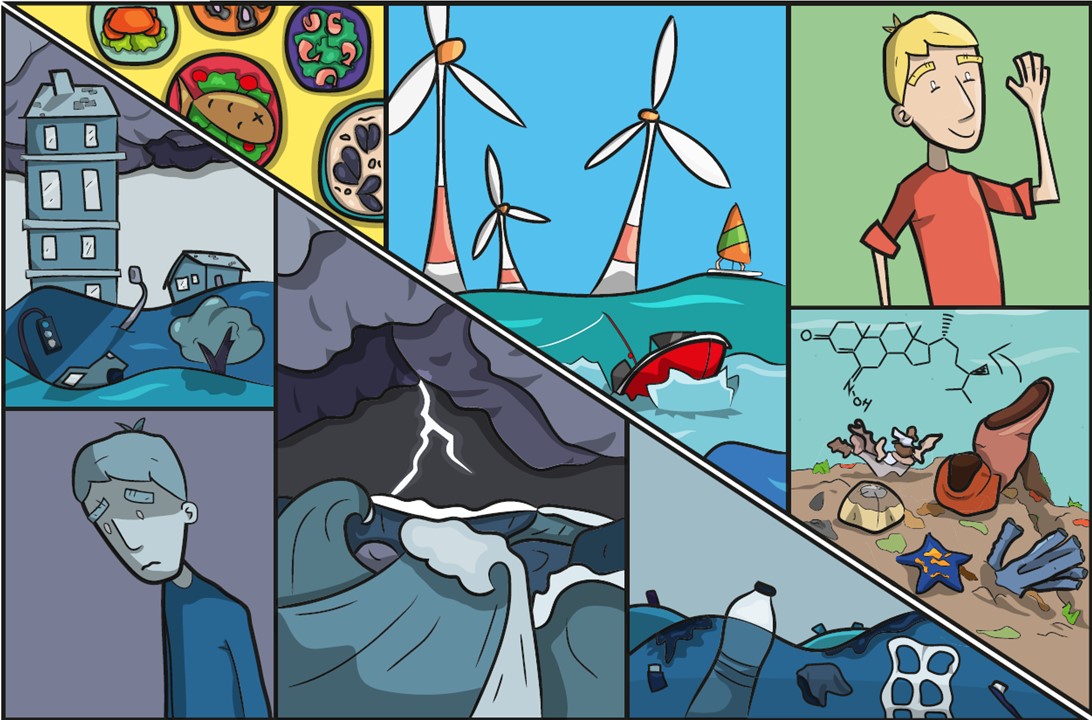



















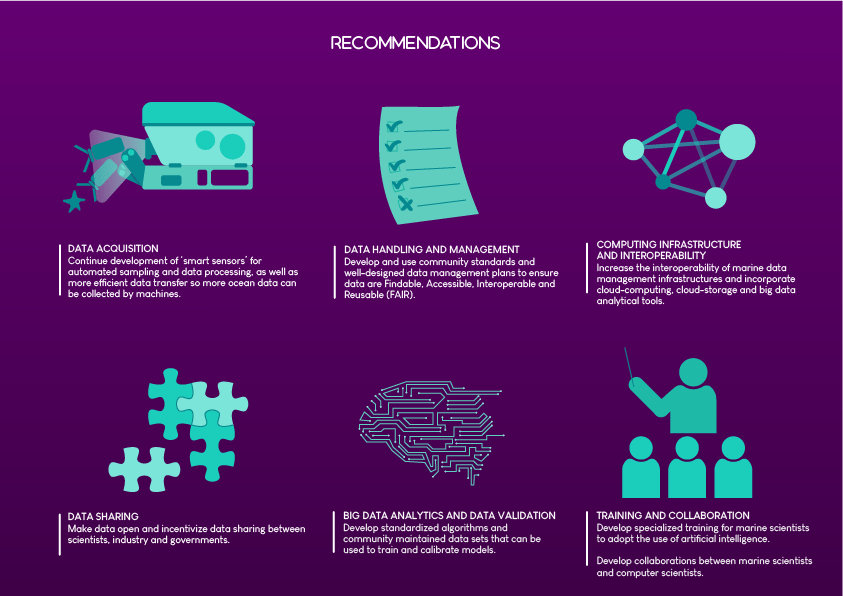
 The Policy Brief on Policy Needs for Oceans and Human Health summarizes the policy challenges when attempting to address both ocean and human health together, and the cooperation and research needed to enable those challenges to be addressed. It proposes ways in which the existing regulatory framework could be adapted to incorporate Oceans and Human Health. It also provides recommendations relating to data and indicators, monitoring, funding and training.
The Policy Brief on Policy Needs for Oceans and Human Health summarizes the policy challenges when attempting to address both ocean and human health together, and the cooperation and research needed to enable those challenges to be addressed. It proposes ways in which the existing regulatory framework could be adapted to incorporate Oceans and Human Health. It also provides recommendations relating to data and indicators, monitoring, funding and training.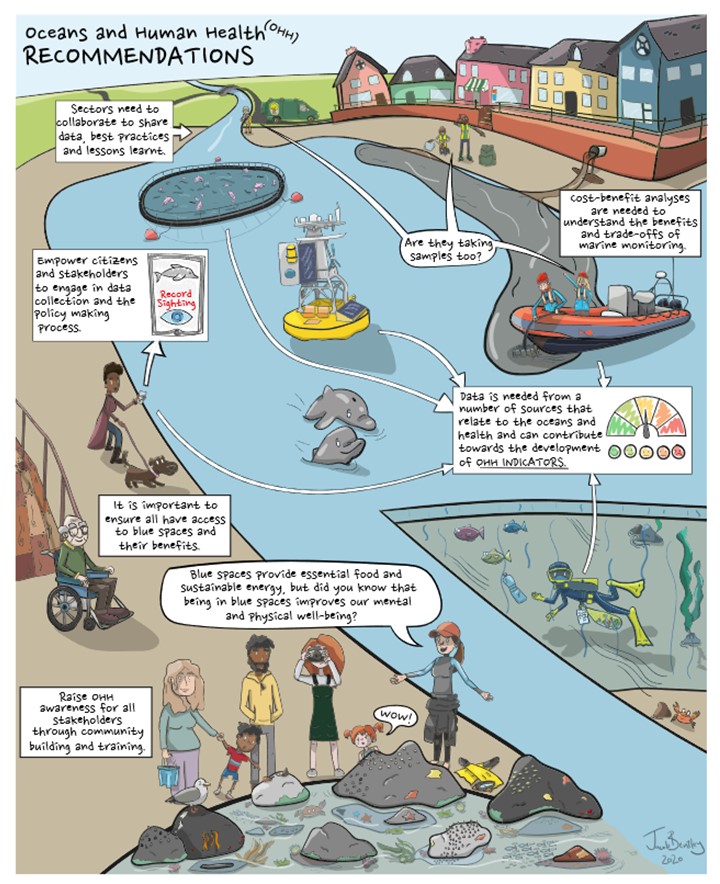
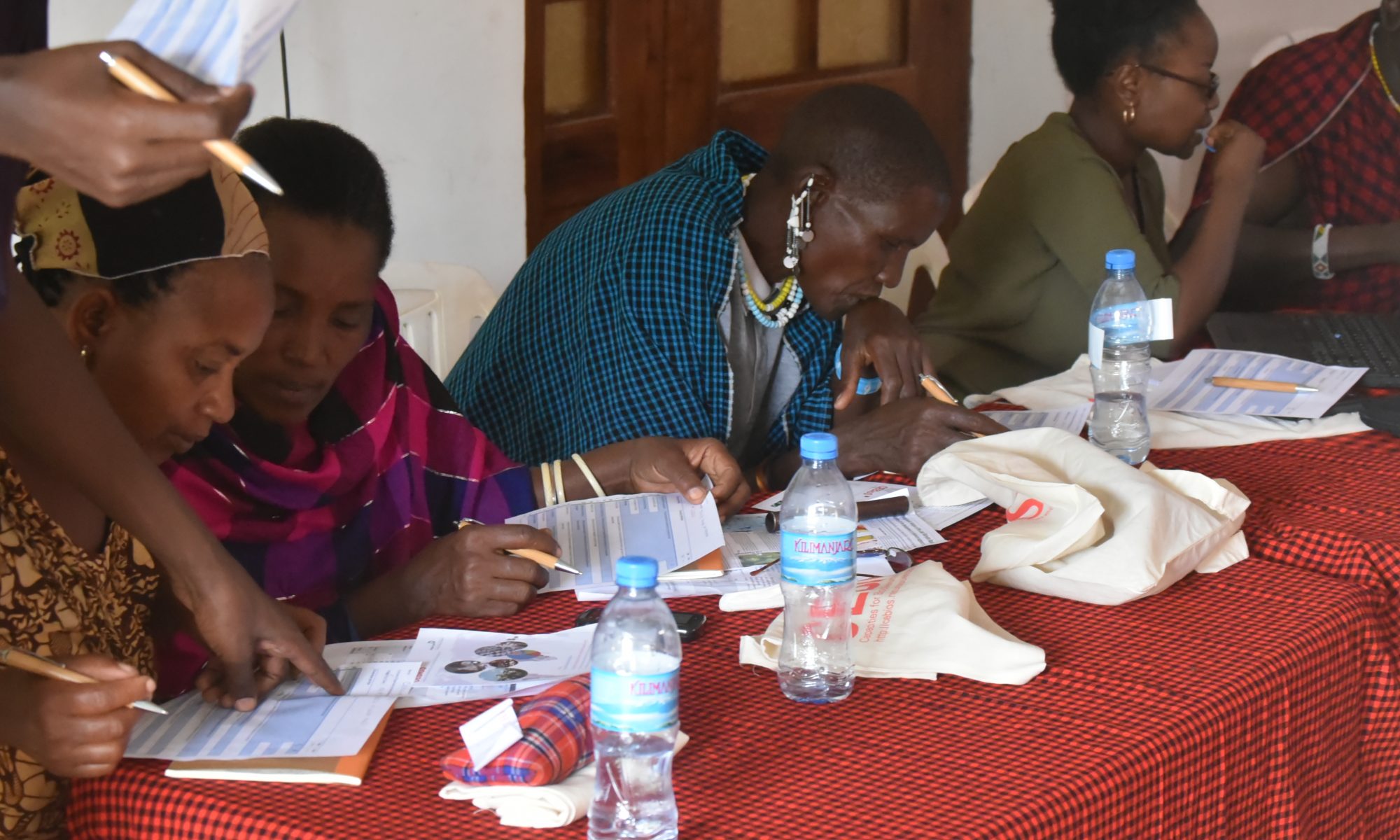
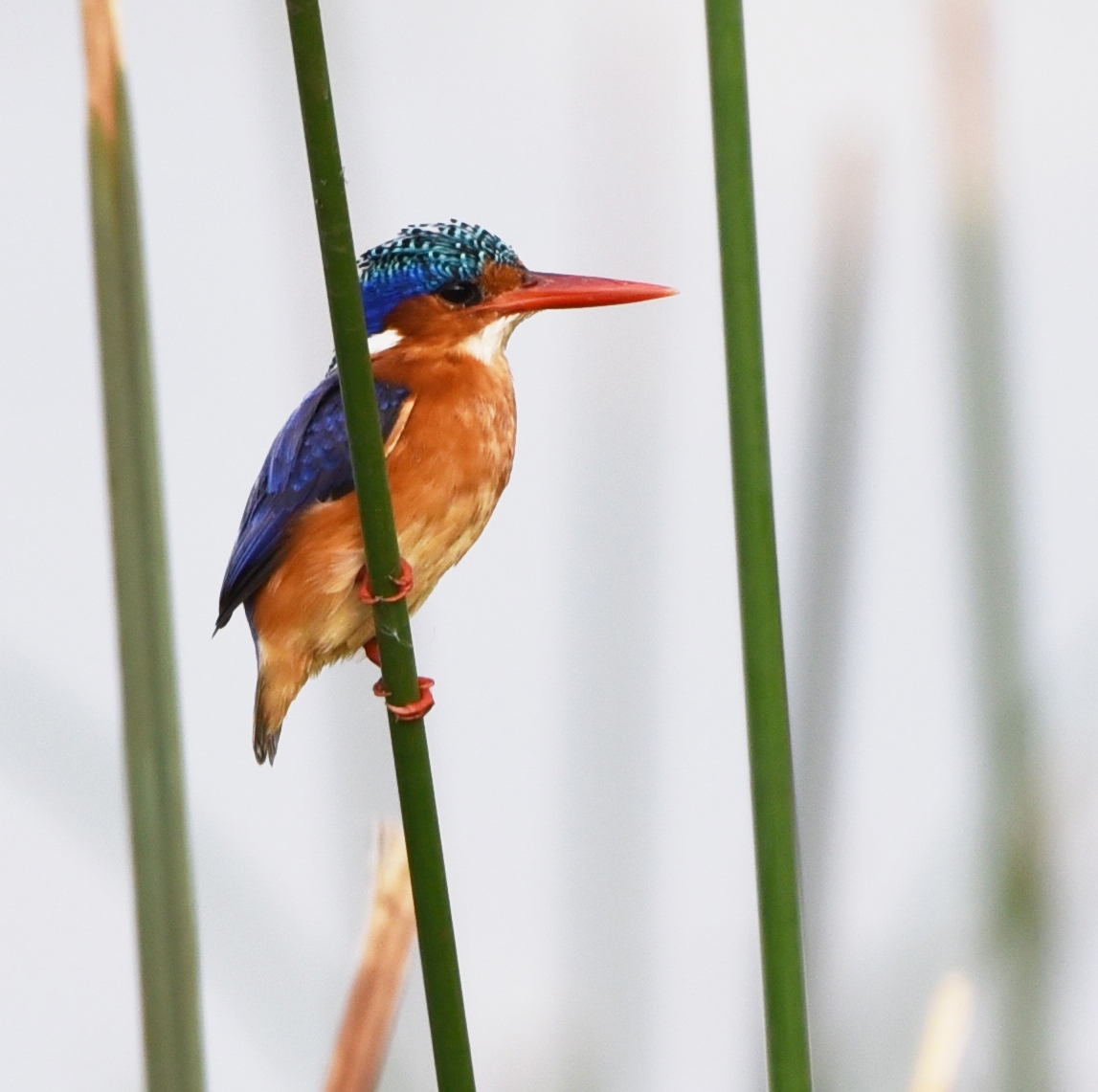
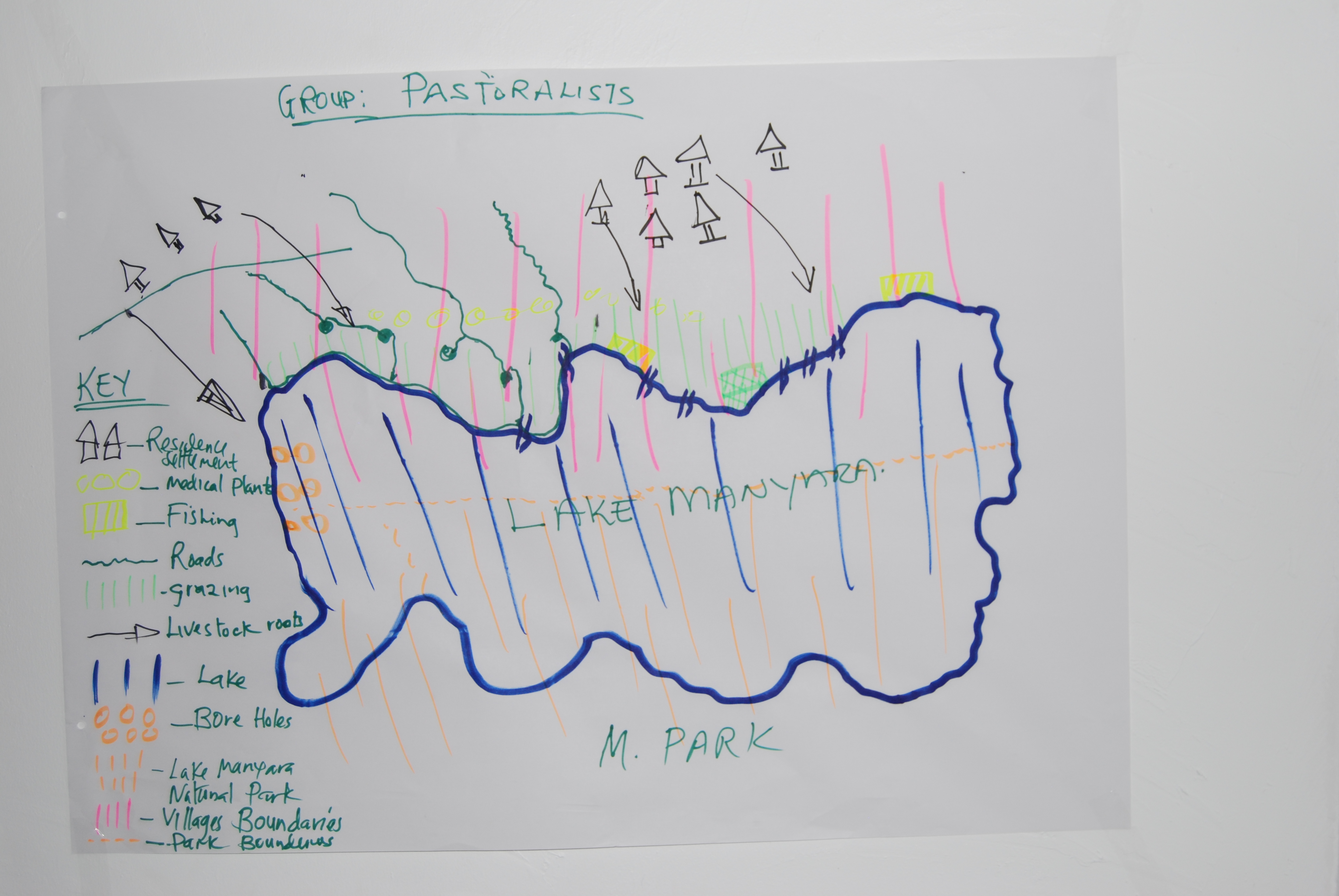







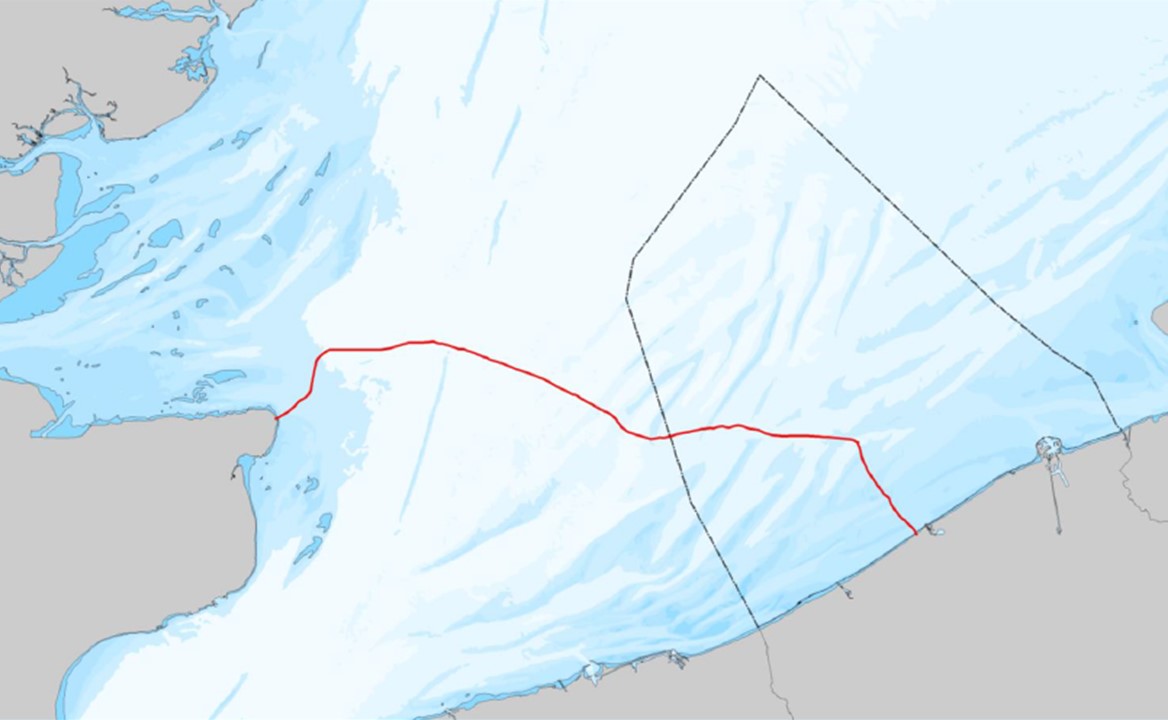
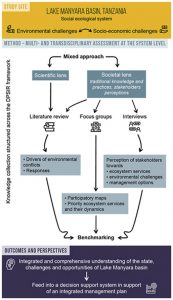 The challenge for scientists and managers lies in reconciling the needs of the local population with the need for the protection of biodiversity. The research that was conveyed in order to identify key actions for the development of the Lake Manyara Basin suggests a unique plural and multifocal approach. This was the outcome of two participative workshops in December 2015 and 2016 that gathered 40 participants and 13 structures from several scientific disciplines, NGOs, local user groups and managers. Together, the participants identified 12 issues which have to be addressed: demographical factors, siltation, erosion, river dry-up, deforestation, destruction of water sources, human activities near the lake, water capture before the water reaches the lake, heavy rainfall causing erosion, evaporation, trampling and grazing. Subsequently, a decision support system in service of an integrated management plan was suggested. The results were published in the
The challenge for scientists and managers lies in reconciling the needs of the local population with the need for the protection of biodiversity. The research that was conveyed in order to identify key actions for the development of the Lake Manyara Basin suggests a unique plural and multifocal approach. This was the outcome of two participative workshops in December 2015 and 2016 that gathered 40 participants and 13 structures from several scientific disciplines, NGOs, local user groups and managers. Together, the participants identified 12 issues which have to be addressed: demographical factors, siltation, erosion, river dry-up, deforestation, destruction of water sources, human activities near the lake, water capture before the water reaches the lake, heavy rainfall causing erosion, evaporation, trampling and grazing. Subsequently, a decision support system in service of an integrated management plan was suggested. The results were published in the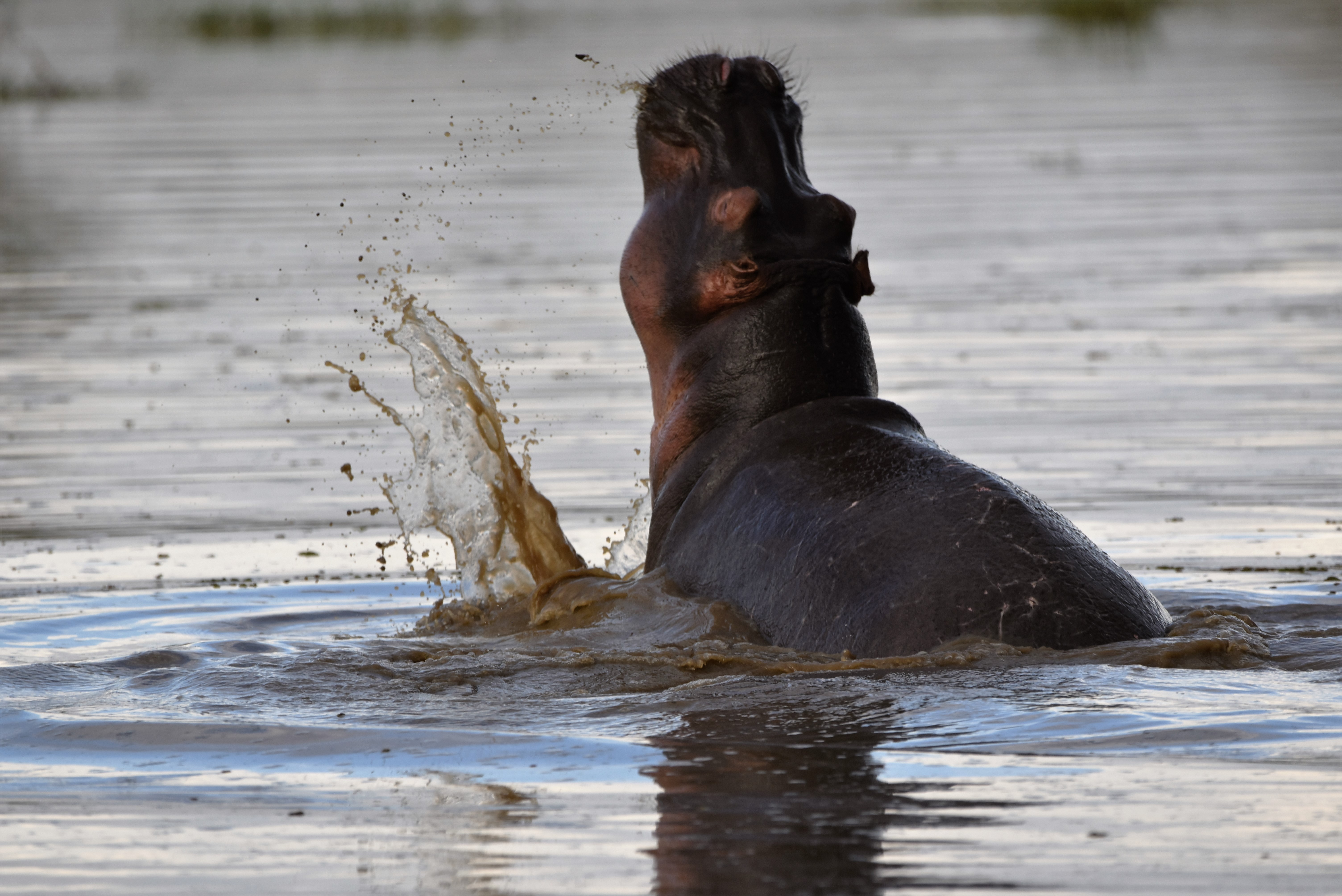 

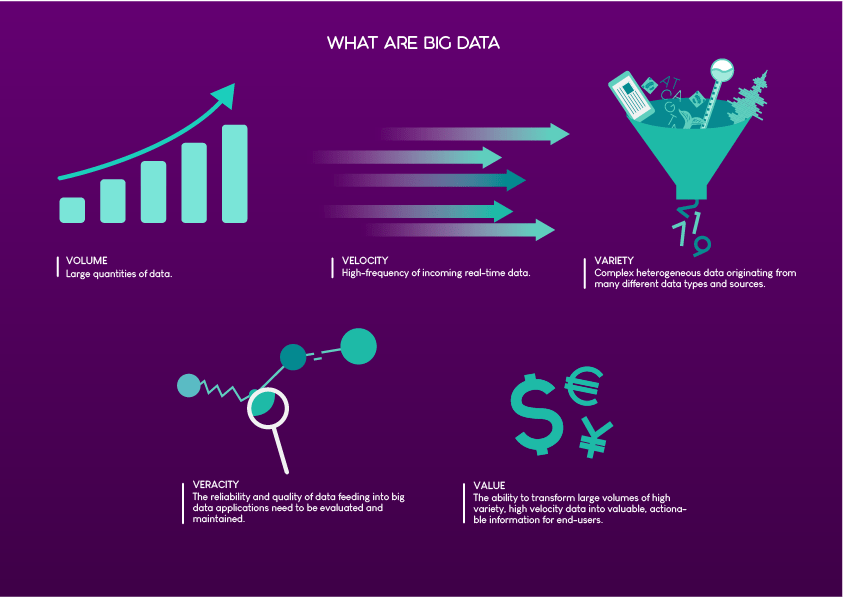
 The European Marine Board’s (EMB) 6th
The European Marine Board’s (EMB) 6th